Hand peripheral nerve surgery
Though occasionally overlooked, few body parts are as crucial to your ability to function than your hands. You use your hands to perform almost every necessary and leisure task. So when you experience any type of hand pain, everyday life can grow far more challenging and unpleasant.
Unfortunately, many types of illnesses and injuries can impact your hands. One such is nerve damage, also known as peripheral neuropathy.
Anatomy
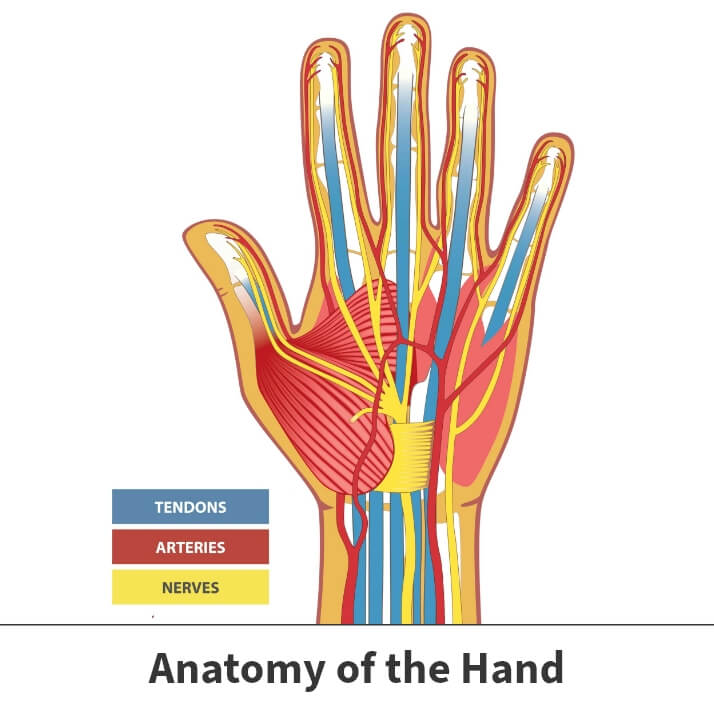
Besides many muscles, bones, and soft tissues, your hands contain nerves. Your hand nerves communicate with the brain and central nervous system to help your body perform various functions. Nerves located in your hands fit into two specific categories, sensory and motor. Sensory nerves enable you to feel sensations like pain, hot, and cold. Motor nerves are responsible for helping you move your hands.
Causes of hand-related nerve damage
Hand-related nerve damage can occur for several different reasons. One of the most common causes is a traumatic injury, such as a significant fall or a car accident. Another common factor is an underlying illness, like:
- Diabetes
- Immune system deficiencies
- Various bacterial or viral infections
- Tumors
- Kidney and liver problems
Hand-related nerve damage can also be caused by alcoholism, repeated exposure to toxic chemicals, chronic use of specific medications, and certain vitamin deficiencies.
Symptoms
Symptoms often vary from person to person and depend on issues, like the exact cause, the condition’s severity, and the extent of the nerve damage.
You may experience common symptoms, including:
- Pain – The intensity may vary, and you might experience other sensations, like burning, jabbing, stabbing, or tingling
- Sensitivity to touch
- Weakness
- The inability to lift, grip, or grasp objects
- Swelling, redness, or inflammation around affected nerve sites
- Partial paralysis
In severe cases, you might experience involuntary movements, such as twitching and tremors.

Diagnosis
Diagnosing nerve damage can be a lengthy and challenging process. During the initial stage, you will receive a thorough physical examination where your doctor will review your medical history, the symptoms you have, lifestyle habits, potential exposure to toxins, and the medications you take. If nerve damage is suspected, your doctor will perform neurological tests designed to measure your reflexes and the ability to feel certain sensations.
Should your healthcare provider suspect nerve damage related to a potentially undiagnosed illness, they can use diagnostic tools, such as:
- Body scans – Imaging tests, such as Magnetic Resonance Imaging, or MRI, Computerized Tomography (CT scans), enable your doctor to capture images designed to reveal nerve damage or other serious issues.
- Blood tests – The presence of several diseases, such as diabetes, immune system disorders, and vitamin deficiencies, can be detected through simple blood tests.
Treatment
Your doctor will choose the most appropriate form of treatment after considering several key issues, such as the specific cause, how pronounced the condition is, and the severity of associated symptoms.
Nonsurgical treatment options
In less severe cases of hand-related nerve damage, your doctor might use any one of the following nonsurgical treatment options:
- Watchful waiting – If your doctor cannot formally diagnose any underlying condition and the damage is not significant, they might suggest a period of observation to see if the issue improves.
- Medications – In mild to moderate instances, your doctor might recommend using over-the-counter non-steroidal inflammation-reducing or pain-alleviating medications, such as Advil/Motrin (ibuprofen) and Aleve (naproxen). Should your case be more serious and produce higher levels of discomfort, your healthcare provider may prescribe other medications.
- Nerve stimulation – In moderate to severe cases, you might be a candidate for Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS). During this process, your physician places electrodes on the affected hand, and small doses of electrical currents are sent through the skin.
- Physical therapy – If your hands experience weakness or mobility issues, physical therapy may be used. A licensed physical therapist orchestrates a program geared towards helping your hands regain strength and mobility.
- Peripheral nerve surgery hand – The most severe manifestations often cause nerve compression. In such circumstances, you might benefit from a procedure known as nerve decompression. During this intervention, a surgeon alleviates the pressure on impacted nerves.
Related specialties
- Basal Joint Surgery
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
- De Quervain's Tenosynovitis
- Dislocated Finger
- Distal Radius Fracture (Broken Wrist)
- Dupuytren’s Disease
- Flexor Tendonitis
- Fractured Fingers
- Functional Nerve Transfers of the Hand
- Ganglion Cysts
- Hand & Finger Replantation
- Hand Nerve Decompression
- Hand Skin Grafts
- Nerve Pain
- Revascularization of the Hand
- Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Hand
- Sports Wrist & Hand Injuries
- Sprained Wrist
- Sudden Acute Finger, Hand & Wrist Injuries
- Targeted Muscle Reinnervation (TMR)
- Tendon Transfers of the Hand
- Thumb Ulnar Collateral Ligament Injuries
- Trigger Finger
- Ulnar Neuritis
- WALANT (Wide Awake Local Anesthesia No Tourniquet)
- Wrist Arthroscopy
- Wrist Fractures
- Wrist Tendonitis
