Vertebroplasty
Vertebroplasty is a procedure where a special type of cement is injected into a vertebra after it has been fractured. When the spine has been injured, it is crucial to work as quickly as possible to diagnose the injury. Vertebroplasty is only recommended when all other nonsurgical treatment options are exhausted.
Anatomy
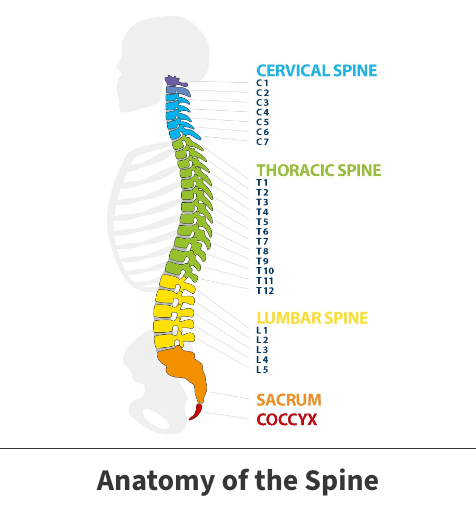
Vertebrae are 33 individual bones that interlock to form the spinal column. The vertebrae are categorized into regions:
- Cervical
- Thoracic
- Lumbar
- Sacrum
- Coccyx
While each region does have separate features, they have three main parts: body, vertebral arch and processes for muscle attachment. If injured, these vertebrae can create intense pain and decrease mobility.
About
Vertebroplasty is only recommended if the fracted vertebrae has inferred with the patient’s daily life physically, emotionally or socially. If left untreated, fractured vertebrae can create more serious issues such as respiratory problems, deep vein thrombosis, osteoporosis, and loss of height. Vertebroplasty can prevent these complications as well as allow for the patient to heal faster and regain movement.
Symptoms
Vertebroplasty is performed when a vertebra has fractured. Symptoms of a fractured vertebrae include:
- Sudden onset of pain in the back
- Limited mobility of the spine
- Height loss
- Worsened pain when standing or walking
- Lessened pain when lying down on one’s back
For those who perform daily tasks at work or during everyday life that require lifting or bending, a fractured vertebra is much more common. Fractured vertebrae can also occur after a fall.
Diagnosis
Your Florida Orthopaedic Institute physician will evaluate your symptoms and determine the cause of your pain. In some cases, vertebroplasty is not necessary if symptoms are not severe. Your physician will ask about your daily routine and any activities which make the pain feel worse. They may also have you lie down flat to determine if the pain is lessened in that position. Additionally, imaging tests such as MRIs or CT scans may be ordered to see where the fractured vertebra is located.
Treatment
Your physician will discuss with you all options for your treatment to determine which is the best for your needs. Vertebroplasty is a surgical procedure, but non-surgical procedures can also ease pain depending on severity. Tell your physician if you are taking any blood thinners or have a history of bleeding disorders, as this could affect blood clotting. Additionally, discuss with them all over-the-counter medicine and herbal supplements you take.
Nonsurgical treatments
Florida Orthopaedic Institute physicians provide all non-surgical options to a patient before surgery being recommended. Since vertebroplasty is a surgical treatment, it is only recommended if the pain is severe or interferes with the patient’s daily life.
If the pain is not as severe, nonsurgical treatment methods may be used to reduce the pain of the fractured vertebra. These may include:
- Back braces
- Physical therapy
- Muscle relaxants
- Pain relievers
- Bed rest
Surgical treatments
Depending on the severity of the fractured vertebra and the nature of the pain, your physician may recommend vertebroplasty.
Since a special cement is inserted into the fractured vertebra, sedation medicine or general anesthesia may be used to calm and relax the patient during the procedure. Depending on how the cement enters the vertebra, a second injection may be required.
After the procedure, your physician will likely have you lie on your back for an hour while the cement hardens. Pain relief may be immediate, or it could take up to 72 hours. Over-the-counter pain relievers can help ease discomfort. A back brace may need to be worn after the procedure, but it is usually unnecessary.
Videos
Related specialties
- Anterior Cervical Corpectomy & Discectomy
- Artificial Disc Replacement (ADR)
- Bone Cement Injection
- Degenerative Disc Disease
- Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH)
- Discectomy
- Discitis Treatment & Information
- Epidural Injections for Spinal Pain
- Foraminotomy
- Interlaminar Implants
- Interlaminar Lumbar Instrumental Fusion: ILIF
- Kyphoplasty (Balloon Vertebroplasty)
- Kyphosis
- Laminectomy: Decompression Surgery
- Lumbar Epidural Steroid Injection
- Lumbar Interbody Fusion (IBF)
- Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery
- Outpatient Spine Surgery
- Pinched Nerve
- Piriformis Syndrome
- Sacroiliac Joint Pain
- Sciatica
- Scoliosis
- Spinal Fusion
- Spondylolisthesis & Spondylolysis
- Whiplash & Whiplash Associated Disorder (WAD)
