Aspiration of the olecranon bursa
Fluid in the elbow
Aspiration of the olecranon bursa is a procedure that removes fluid from the sac in the elbow, known as the olecranon bursa. The olecranon bursa can fill with fluid in elbow and swell due to a variety of reasons such as an injury, infection, and prolonged pressure. Aspiration of the olecranon bursa is used as a way for your physician to determine the type of infection you have. Once your physician determines the type of infection, they can prescribe to you the correct type of antibiotic so that you can make a quick and smooth recovery.
Anatomy
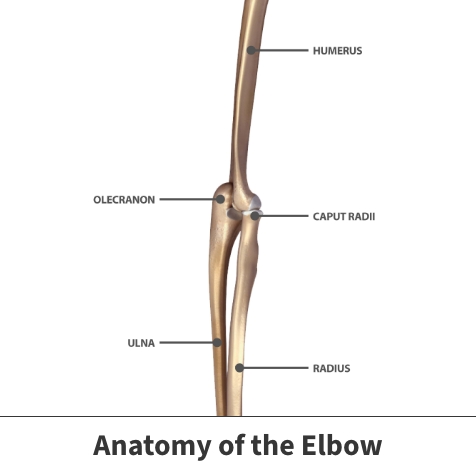
The elbow joint is where the upper arm bone (humerus) meets the two forearm bones (radius and ulna). The bony point of the elbow is the olecranon, located at the upper end of the ulna. The elbow consists of several muscles, ligaments, nerves, and tendons, and is both a pivot and hinge joint, meaning it allows you to bend and straighten, as well as twist and rotate your arm. The olecranon bursa is positioned directly under the elbow skin and has very little protection from muscles or other soft tissues.
The olecranon bursa is a thin, fluid-filled sac located at the bony tip of the elbow (olecranon). This sac allows the soft tissues to move freely over the underlying bone.
About the procedure
Aspiration of the olecranon bursa is a nonsurgical procedure used to remove fluid from the olecranon bursa. Normally the olecranon bursa is flat. If it becomes irritated or inflamed, more fluid will accumulate in the bursa, causing it to swell, and that fluid may need to be drained to prevent any further injury in the elbow. This condition is known as elbow bursitis.
Several factors can cause elbow bursitis, including:
- Trauma – A hard blow to the tip of the elbow can cause the bursa to produce excess fluid and swell.
- Infection – If an injury at the tip of the elbow breaks the skin, such as an insect bite, scrape, or puncture wound, bacteria may get inside the bursa sac and cause an infection. The infected bursa produces fluid, redness, swelling, and pain. If the infection goes untreated, the fluid may turn to pus.
- Prolonged pressure – Leaning on the tip of the elbow for long periods on hard surfaces, such as a tabletop, may cause the bursa to swell and fill with fluid.
- Medical conditions – Certain conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis and gout, are associated with elbow bursitis.

Treatment
If your Florida Orthopaedic Institute physician thinks that your elbow bursitis is caused by an infection, they may recommend an aspiration of the olecranon bursa. This is commonly done as an office procedure with a needle. Fluid removal not only helps to decrease swelling of the olecranon bursa, but will also give your physician a sample of the fluid that can be looked at in a laboratory to identify if any bacteria are present. This lets your physician know if a specific antibiotic is needed to fight the infection.
Depending on the severity of the infection, your physician may prescribe antibiotics to prevent the infection from getting any worse.
Videos
Related specialties
- Arthroscopic Debridement of the Elbow
- Cubital Tunnel Syndrome
- Elbow Bursitis
- Elbow Injuries & Inner Elbow Pain in Throwing Athletes
- Golfer's Elbow
- Growth Plate Injuries of the Elbow
- Hyperextension Injury of the Elbow
- Little Leaguer's Elbow (Medial Apophysitis)
- Olecranon Stress Fractures
- Radial Tunnel Syndrome
- Tennis Elbow Treatment
- Tricep Pain & Tendonitis
- UCL (Ulnar Collateral Ligament) Injuries
- Valgus Extension Overload
