Wrist tendonitis
Wrist tendonitis is a common condition that can occur due to everyday activity and motion. Usually affecting a single tendon, wrist tendonitis occurs when a tendon becomes inflamed and irritated. The point where the tendons in the wrist cross is the most likely to be irritated, but with proper treatment can usually heal without issue.
Anatomy
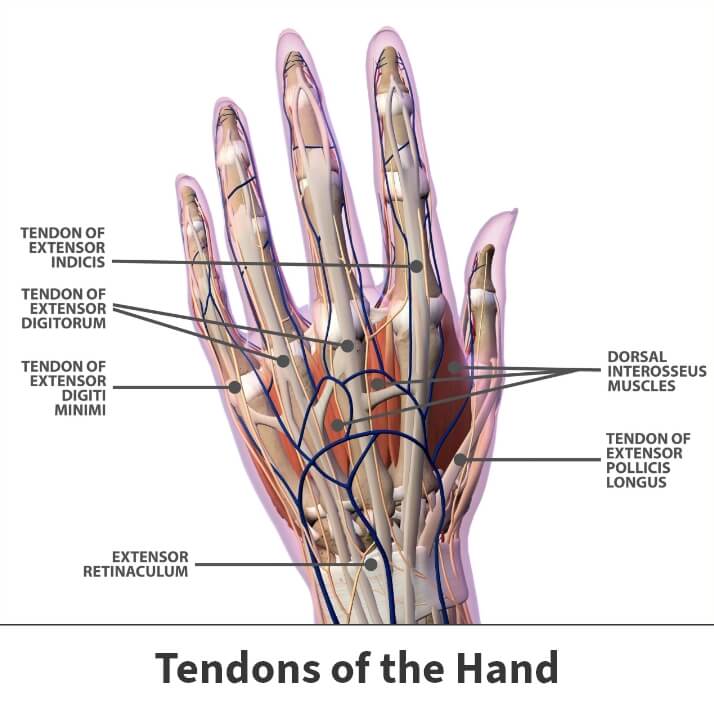
Tendons connect muscle to bone, and wrist tendons connect forearm muscles to bones in the hand. The tendons slide through sheaths inside of the wrist. These sheaths have a fluid inside called synovial fluid, and when this becomes inflamed, it is known as tenosynovitis.
The tendons around the wrist are in two groups:
- Extensors – Back of the wrist
- Flexors – Front of the wrist
Any of the tendons can become inflamed, but it is more likely to occur in tendons that are used more often in daily activity.
About
Wrist tendonitis is caused by overuse of the wrist and the tendons that make up the wrist. This overuse does not only come from physical activity, but everyday activities such as typing. Tennis players are a group that also suffer from wrist tendinitis, as they are much more likely to put a strain on their tendon.
Since wrist tendonitis applies to the early stages of tendon inflammation, it is quicker to heal than tenosynovitis – the advanced stage of inflammation.
Symptoms
The most common symptom of wrist tendonitis is pain in and around the wrist area. This pain generally worsens when performing activities involving the wrist. Other symptoms include:
- Warmth of tendons
- Redness of tendons
- Grinding sensations
- Swelling around the wrist joint
Diagnosis
Your Florida Orthopaedic Institute physician will discuss your diagnosis with you and the best possible treatment options for your injury. The diagnosis of wrist tendonitis is generally made by examining the wrist and evaluating your symptoms. Your physician will ask about your activity history and if you are experiencing any pain.
A test to stretch the tendons may allow for your physician to see where the pain is coming from in the wrist.
Your physician may also order X-rays and other diagnostic tests to evaluate the cause of the wrist pain, if the cause is unknown. Since most people with wrist tendonitis have a normal X-ray, this can allow for the physician to determine if outside factors such as arthritis or fractures come into play.
Treatment
Once a diagnosis has been made, your physician will go over the treatment options that best fit you and your injury. Since almost all injuries vary, treatment also varies from person to person. Almost all treatments start with immobilization to allow for stabilization of the injury. From there, your physician will determine the severity and make a recommendation about treatment.
Nonsurgical treatments
Your Florida Orthopaedic Institute physician will take the appropriate steps to determine if nonsurgical treatment options can be utilized before surgery. Their recommendations for nonsurgical treatments may include:
- Ice – To help cool down inflammation and increase blood flow
- Anti-inflammatory medicine – Control symptoms of pain and decrease inflammation and swelling
- Hand therapy – Physical therapy focused on the tendons and ligaments to make them stronger
- Cortisone injection – Injected directly to the inflamed area to make it subside
Surgical treatments
Surgery is only recommended when all other nonsurgical treatment options have been exhausted. In the surgical procedure, inflammatory tissue can be removed to create more space for the tendon to move freely through the sheath. In this case, the area of tendon sheath causing the issues can be removed.

Related specialties
- Basal Joint Surgery
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
- De Quervain's Tenosynovitis
- Dislocated Finger
- Distal Radius Fracture (Broken Wrist)
- Dupuytren’s Disease
- Flexor Tendonitis
- Fractured Fingers
- Functional Nerve Transfers of the Hand
- Ganglion Cysts
- Hand & Finger Replantation
- Hand Nerve Decompression
- Hand Skin Grafts
- Nerve Pain
- Peripheral Nerve Surgery (Hand) Revision
- Revascularization of the Hand
- Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Hand
- Sports Wrist & Hand Injuries
- Sprained Wrist
- Sudden Acute Finger, Hand & Wrist Injuries
- Targeted Muscle Reinnervation (TMR)
- Tendon Transfers of the Hand
- Thumb Ulnar Collateral Ligament Injuries
- Trigger Finger
- Ulnar Neuritis
- WALANT (Wide Awake Local Anesthesia No Tourniquet)
- Wrist Arthroscopy
- Wrist Fractures
